- This topic is empty.
-
AuthorPosts
-
2026-01-09 at 5:48 pm #8213
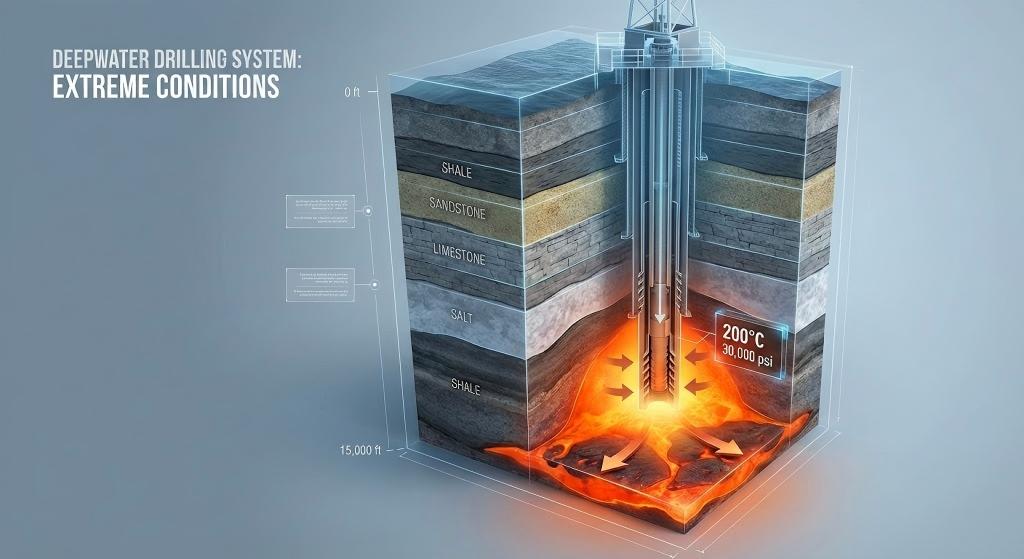
Why HPHT Environments Destroy Standard Steel Balls
The Destructive Trio: Temperature + Pressure + Corrosion
Downhole environments create unique stressors:
-
Temperature: HPHT wells operate at 150-200°C (302-392°F), with some ultra-deep formations exceeding 230°C
-
Pressure: Hydrostatic loads reach 20,000-30,000 psi in deepwater drilling operations
-
Corrosive media: Hydrogen sulfide (H₂S), carbon dioxide (CO₂), and chloride-rich formation water
Material Failure: GCr15 vs S2 at Elevated Temperatures
Traditional chrome steel balls (GCr15/52100) lose hardness above 120°C due to tempering effects:
Temperature GCr15 Hardness (typical) S2 Tool Steel Hardness 25°C HRC 62-64 HRC 58-60 150°C HRC 55-57 HRC 57-59 200°C HRC 48-52 HRC 56-58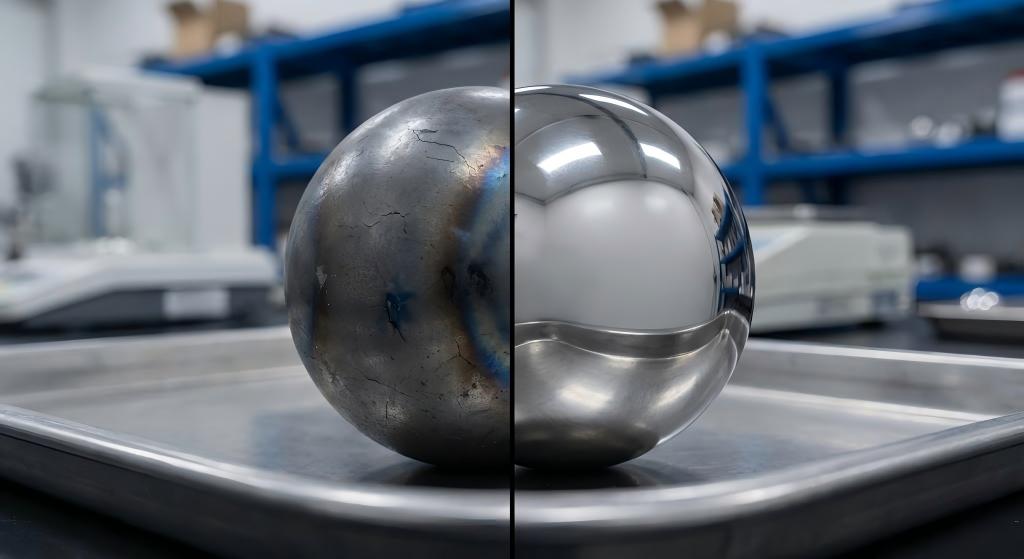 
Critical insight: S2's molybdenum content (0.40-0.60%) provides superior tempering resistance, maintaining structural stability where bearing steels experience metallurgical degradation.
H₂S-Induced Cracking: Field Failure Analysis
A North American drilling contractor (confidential client, internal test report EST-2019-047 available upon request) experienced valve failure in their blowout preventer (BOP) check valve after only 180 operational hours. Post-failure metallurgical analysis revealed:
-
Sulfide stress cracking (SSC) on 440C stainless steel balls (hardness HRC 58)
-
Micro-pitting at ball-seat contact surfaces under cyclic pressure (15,000 psi)
-
Geometry distortion (out-of-roundness increased from initial 2.5μm to 12μm)
Test conditions: Formation water with 5,000 ppm H₂S, 150°C operating temperature, 500+ pressure cycles per day.
Switching to S2 tool steel balls (heat-treated to HRC 58-60) extended service life to 1,200+ hours with no detectable cracking—a 567% improvement under identical operating conditions.
S2 Material Advantages for Subsea Valves
Impact Toughness: The Hidden Performance Factor
While hardness matters, impact resistance is critical during:
-
Pressure surges from formation kicks (sudden influx events)
-
Hydraulic hammering in mud circulation systems
-
Thermal shock during emergency well control operations
S2 tool steel delivers superior toughness compared to high-carbon bearing steels:
-
Charpy impact value: 18-22 J/cm² (vs 8-12 J/cm² for fully hardened GCr15)
-
Fracture resistance: Lower brittleness under instantaneous shock loads
This is why S2 is increasingly specified for subsea valve assemblies where sudden pressure differentials are routine.
Sour Service Considerations: NACE MR0175/ISO 15156
Important compliance note: NACE MR0175/ISO 15156 standards for sour service have strict hardness limitations—many carbon and low-alloy steels must not exceed 22 HRC to minimize SSC risk in H₂S environments.
S2 tool steel balls, when heat-treated to HRC 58-60, fall outside this hardness range. However, they may still be evaluated through:
-
Material qualification testing per NACE TM0177 (laboratory SSC testing)
-
Site-specific risk assessment based on H₂S partial pressure, temperature, and pH
-
Engineering critical assessment (ECA) by qualified corrosion engineers
Recommendation: For applications requiring NACE compliance, consult with corrosion specialists and consider additional protective measures such as coatings or alloy selection review. S2's performance advantage lies in impact resistance and temperature stability, not absolute corrosion immunity.
Quality Control for Oilfield Applications: The Changzhou Eurasian Advantage

CQI-9 Heat Treatment Certification
Our self-owned CQI-9 compliant heat treatment line ensures batch-to-batch consistency critical for oilfield components:
Quenching process: Controlled austenitizing at 870-900°C, oil quench to achieve uniform martensite transformation
Tempering protocol: Double tempering at 520-550°C maintains HRC 58-62 while maximizing toughness
Result: Hardness deviation within ±1 HRC across production lots—essential for automated assembly in valve manufacturing.
Material Traceability & PMI Testing
Every batch undergoes positive material identification (PMI) using our in-house optical emission spectrometer:
-
Chemistry verification: Confirms S2 composition per ASTM A681
-
Sulfur/phosphorus control: <0.025% each (minimizes inclusion-related failures)
-
Trace element analysis: RoHS compliance verification
Our Bureau Veritas (BV) certification enables third-party inspection and witness testing—a requirement for Tier 1 oil service contractors.
Dimensional Precision for Seal Integrity
Downhole valves demand zero-leakage seals under extreme pressures. Our quality laboratory validates:
-
Sphericity (via roundness tester): Grade G100 per ABMA Std-10 (2.5μm deviation maximum)
-
Surface finish: Ra <0.05μm via profilometer measurement
-
Diameter consistency: ±2.5μm tolerance across production batch
Why this matters: Even minor geometry deviations can cause micro-leakage under 20,000+ psi, allowing drilling mud bypass and catastrophic valve failure.
Case Study: Extending Valve Life in Permian Basin Horizontal Wells
The Challenge
A Permian Basin operator (Texas, USA – client name confidential, test report PB-2021-033 available upon NDA) experienced recurring check valve failures in downhole safety valves (DSV) during hydraulic fracturing operations.
Failure pattern: Average service life of only 8 frac stages (approximately 45 days) before ball surface degradation.
Root cause analysis: Ball surface spalling due to proppant-laden fluid erosion (30 mesh sand at 2 lb/gal concentration) combined with thermal cycling (ambient 25°C to downhole 150°C).
Previous material: Hardened 440C stainless steel balls, 9.525mm (3/8 inch) diameter
The Solution
Material substitution to S2 tool steel balls with optimized specifications:
-
Material: S2 heat-treated to HRC 60 ±1
-
Size: 9.525mm (3/8 inch) precision ground
-
Grade: G100 per ABMA Std-10
-
Documentation: Full PMI test report + heat treatment curves
The Results (45-well field trial, 18-month duration)
-
Service life extension: From 8 stages to 28+ stages average (250% improvement)
-
NPT reduction: Eliminated 12 unplanned workovers per well
-
Cost impact: Estimated savings of $1.2M-$1.8M per well in avoided NPT (based on operator's internal rig rate of $50K-$75K per day)
-
Seal reliability: Zero reported leakage incidents across 45-well test program
Project engineer feedback (anonymized): "The combination of impact resistance and hardness retention under thermal cycling made S2 the clear winner over both 440C and GCr15. We've now standardized S2 for all our completions fleet DSV assemblies."
Technical Specifications: S2 Tool Steel Balls
Material Composition (ASTM A681 – Type S2)
Note: Composition ranges below reflect typical "Type Analysis" from major steel mills. Actual chemistry may vary slightly by supplier.
Element Percentage Function Carbon (C) 0.45-0.55% Base hardenability Silicon (Si) ≤1.0% Deoxidizer, slight tempering resistance Manganese (Mn) 0.30-0.50% Hardenability enhancement Chromium (Cr) 0.30-0.50% Wear resistance Molybdenum (Mo) 0.40-0.60% High-temperature strength retention Vanadium (V) 0.15-0.30% Grain refinement Heat treatment classification: Water-hardening tool steel with secondary hardening characteristics.
Available Sizes & Tolerances
-
Diameter range: 1.588mm (1/16") to 50.800mm (2")
-
Standard grades: G100, G200, G500 (per ABMA Std-10 / ISO 3290)
-
Custom specifications: Available for API 6A wellhead equipment or customer-specific requirements
Mechanical Properties (As Heat-Treated)
-
Hardness range: HRC 58-62 (application-dependent tempering)
-
Core toughness: Charpy impact 15-22 J/cm² (at HRC 60)
-
Compressive strength: >2,500 MPa
Comparative Analysis: Material Selection Guide
When to Choose S2 Over Alternatives
S2 Tool Steel is optimal for:
-
HPHT wells (operating temperatures >120°C, pressures >10,000 psi)
-
High-cycle applications (valve open/close cycles >500 per day)
-
Impact-dominated failures (pressure surges, hydraulic shock)
-
Cost-performance balance (when tungsten carbide is cost-prohibitive)
Consider alternatives when:
-
440C stainless steel: If corrosion resistance is paramount and impact loads are low (<100°C, minimal cycling)
-
Tungsten carbide: If abrasion dominates and budget allows (significantly higher cost)
-
Ceramic balls (Si₃N₄): For ultra-high temperature (>250°C) with minimal impact risk
Cost-Performance Considerations
While we cannot publish specific pricing (varies by order quantity, size, and market conditions), general positioning:
-
S2 tool steel: Moderate cost premium over bearing steels, justified by extended service life in HPHT applications
-
Service life advantage: Field data suggests 2-3× longer valve life compared to hardened bearing steels in thermal cycling environments
-
TCO (Total Cost of Ownership): Factor in NPT costs, replacement frequency, and logistics when evaluating material selection
ROI example: For offshore operations where NPT costs $500K/day, extending valve service by even 30 days through better material selection can justify substantial material cost differences.
FAQ: S2 Tool Steel Balls for Downhole Applications
Q1: What is the maximum operating temperature for S2 steel balls in downhole tools?
A: S2 tool steel balls can operate continuously up to approximately 200°C (392°F) while maintaining hardness in the HRC 56-58 range. At 150°C, hardness retention exceeds 95% of room-temperature values. For applications routinely exceeding 230°C, ceramic balls (Si₃N₄) or specialized high-temperature alloys should be evaluated.
Q2: Can S2 balls be used in NACE MR0175 sour service environments?
A: S2 balls heat-treated to HRC 58-60 exceed the typical 22 HRC hardness limit specified in NACE MR0175/ISO 15156 for many carbon and low-alloy steels in sour service. However, S2 may be acceptable through:
-
Material qualification testing per NACE TM0177
-
Site-specific engineering assessment considering H₂S partial pressure, temperature, and pH
-
Use of protective coatings or localized stress relief
Always consult with qualified corrosion engineers before specifying hardened steel balls for sour service applications.
Q3: How does S2 compare to 440C stainless steel for impact resistance?
A: S2 offers significantly superior impact resistance due to its lower carbon content and molybdenum alloying. Typical Charpy impact values:
-
S2 (HRC 60): 18-22 J/cm²
-
440C (HRC 58): 8-12 J/cm²
This makes S2 the preferred choice for applications with pressure surges, hydraulic hammering, or thermal shock, while 440C excels in purely corrosive (non-impact) environments.
Q4: What lead time should we expect for S2 balls with full documentation?
A: Standard sizes (6.35mm to 25.4mm) with G100 grade: 3-4 weeks including heat treatment, testing, and PMI certification. Custom sizes, tighter tolerances (G50), or witness testing requirements: 5-6 weeks. Expedited production available for critical well intervention needs—contact our technical sales team.
Q5: Can you provide third-party witness testing for API 6A certification?
A: Yes. Our Bureau Veritas (BV) factory certification enables on-site witness testing for:
-
Dimensional inspection (diameter, sphericity, surface finish)
-
Hardness verification (Rockwell C scale)
-
PMI analysis (optical emission spectroscopy)
-
Material traceability documentation
Coordinate with our quality team 2 weeks prior to production start to schedule witness inspection.
Partner with a Certified Supplier
At Changzhou Eurasian Steel Ball Co., Ltd, we understand that downhole component failure isn't just an engineering problem—it's a financial and safety crisis. Our combination of:
-
IATF 16949:2016 automotive-grade quality management
-
CQI-9 compliant heat treatment with in-house control
-
Advanced testing laboratory (roundness tester, hardness tester, optical spectrometer, vibration analyzer)
-
Bureau Veritas (BV) factory certification
…ensures every S2 tool steel ball meets the demanding requirements of HPHT oil well applications.
Ready to evaluate S2 balls for your application? Contact our technical sales team for material data sheets, test reports, and sample evaluation programs.
http://www.cnballs.cn
Changzhou eurasian -
-
AuthorPosts
- You must be logged in to reply to this topic.